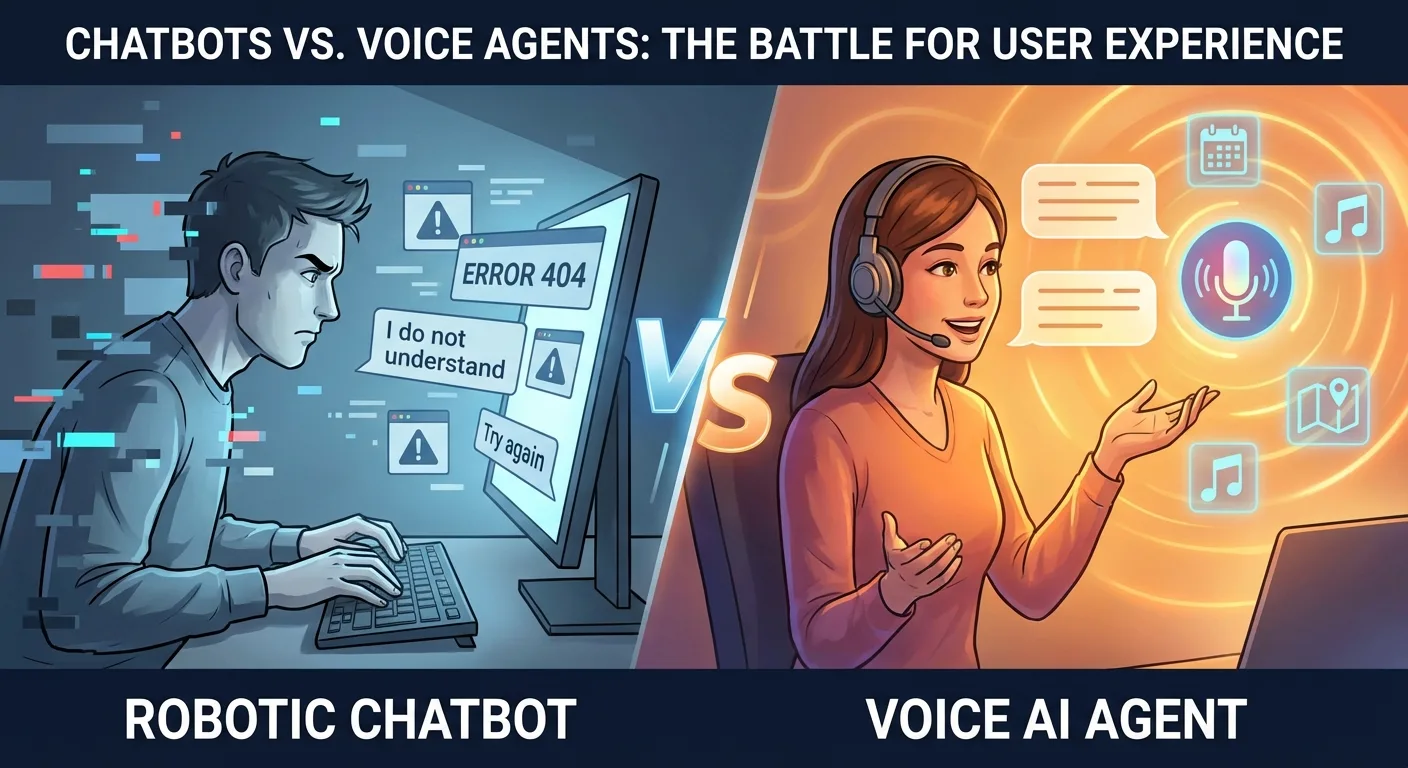
For over a decade, chatbots have been the default answer to scaling customer interactions. Every website seems to have one—that little chat bubble in the corner promising instant assistance. But despite billions invested in chatbot technology, customer satisfaction with these tools remains stubbornly low. Meanwhile, a new category is emerging: voice AI agents that communicate through natural speech rather than typed text. The differences between these approaches are not just technical—they are fundamental to how humans prefer to communicate.
The Chatbot Promise vs Reality
Chatbots promised to revolutionize customer service. The pitch was compelling: instant responses, 24/7 availability, unlimited scalability, and dramatic cost reductions. Companies rushed to implement them.
The reality has been more complicated:
- Customer frustration: Studies consistently show that 70-80% of customers prefer human agents over chatbots
- Limited understanding: Most chatbots struggle with anything beyond simple, predictable queries
- Conversation dead ends: Users frequently hit walls where the bot cannot help and human escalation is required
- Impersonal experiences: Text interactions feel transactional rather than relational
The fundamental problem is not implementation—it is the medium. Text-based chat is simply not how humans naturally communicate.
Why Voice Changes Everything
Voice is humanity is oldest communication technology. We have been speaking for hundreds of thousands of years; we have been typing for barely a century. This evolutionary history matters.
Cognitive Load
Typing requires conscious effort. Users must formulate thoughts into text, correct typos, and parse written responses. Speaking is nearly automatic—we do it without thinking. Voice interactions reduce cognitive load, making communication feel effortless.
Emotional Connection
Voice carries emotional information that text cannot convey. Tone, pacing, emphasis, and warmth all communicate meaning beyond words. When a voice agent responds with appropriate emotion and pacing, it creates connection in ways text never can.
Speed and Efficiency
The average person speaks at 125-150 words per minute but types only 40 words per minute. Voice interactions are 3-4x faster than text. For complex queries, this speed difference compounds dramatically.
Accessibility
Not everyone can type easily. Users with visual impairments, motor difficulties, or simply full hands benefit enormously from voice interfaces. Voice AI democratizes access in ways text chatbots cannot.
Head-to-Head Comparison
Let us compare chatbots and voice agents across key dimensions:
Understanding Natural Language
Chatbots: Parse typed text, often struggling with typos, abbreviations, and non-standard phrasing. Many rely on keyword matching rather than true understanding.
Voice Agents: Modern speech recognition combined with LLMs understands natural speech patterns, accents, and conversational language. Users speak naturally without adapting to the system.
Winner: Voice Agents
Conversation Flow
Chatbots: Interactions feel stilted. Users wait for typing indicators, read responses, formulate replies. The back-and-forth cadence is unnatural.
Voice Agents: Conversations flow like human dialogue. Responses are immediate, interruptions are handled naturally, and the pacing feels right.
Winner: Voice Agents
Complex Queries
Chatbots: Long, complex questions are difficult to type and often misunderstood. Users simplify their queries, losing nuance.
Voice Agents: Users can explain complex situations naturally, with the agent asking clarifying questions as needed. The conversation can go deep.
Winner: Voice Agents
Multi-Tasking
Chatbots: Require visual attention and hand engagement. Users cannot easily chat while doing other things.
Voice Agents: Hands-free operation enables interaction while driving, cooking, or working. The agent can describe what is on screen while users watch.
Winner: Voice Agents
Emotional Intelligence
Chatbots: Cannot detect frustration, confusion, or satisfaction from text alone. Responses are tonally flat.
Voice Agents: Advanced systems detect emotional cues from voice and adjust responses accordingly. A frustrated user gets empathy; an excited user gets enthusiasm.
Winner: Voice Agents
Implementation Complexity
Chatbots: Relatively simple to implement with many off-the-shelf solutions. Lower technical barrier to entry.
Voice Agents: Historically more complex, requiring audio processing, speech recognition, and synthesis. However, modern platforms like Demogod have simplified implementation to single-line integrations.
Advantage: Chatbots (historically), but gap closing rapidly
The Business Case for Voice
Engagement Metrics
Voice interactions show dramatically higher engagement:
- Session duration: 2-3x longer than chat interactions
- Completion rates: 40-60% higher task completion
- Return usage: Users come back to voice experiences more frequently
Conversion Impact
For sales and lead generation, voice outperforms:
- Lead qualification: Voice agents capture richer information through conversation
- Conversion rates: 20-40% higher than equivalent chatbot flows
- Average order value: Voice-guided purchases trend higher due to better recommendation conversations
Customer Satisfaction
The satisfaction gap is significant:
- CSAT scores: Voice interactions consistently score 15-25% higher
- NPS impact: Positive voice experiences drive promoter behavior
- Complaint reduction: Fewer escalations to human agents
Use Cases Where Voice Excels
Product Discovery and Demos
When users need to explore products, voice guidance is transformative. At Demogod, we have seen voice-guided product demos outperform every other demo format. Users can ask questions naturally while the agent navigates and demonstrates—an experience impossible with text chatbots.
Complex Support Queries
When customers have nuanced problems, explaining via voice is dramatically easier than typing detailed descriptions. Voice agents can ask follow-up questions conversationally, building understanding iteratively.
Hands-Free Scenarios
Kiosks, in-car systems, smart home devices, and mobile on-the-go scenarios all favor voice. Users cannot or do not want to type; voice is the natural choice.
Accessibility-First Applications
For users with disabilities, voice interfaces are not just preferred—they are essential. Voice AI makes digital experiences accessible to populations underserved by text interfaces.
When Chatbots Still Make Sense
To be fair, chatbots are not obsolete. They remain appropriate for:
- Simple transactional queries: Order status, account balance, basic FAQ
- Noise-sensitive environments: Open offices, libraries, public transit
- Privacy-sensitive topics: Users may prefer typing about medical or financial issues
- Documented records: Some users want text transcripts of interactions
The best approach is often hybrid: offer both options and let users choose based on context and preference.
The Technology Shift
Several technological advances have made voice agents viable at scale:
Speech Recognition Accuracy
Modern ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) systems achieve near-human accuracy. Accents, background noise, and natural speech patterns are handled gracefully.
Large Language Models
LLMs enable voice agents to understand context, maintain conversation state, and generate natural responses. The reasoning capabilities that make chatbots useful are even more powerful when paired with voice.
Text-to-Speech Quality
Synthetic voices now sound remarkably human. The uncanny valley of robotic speech has been crossed. Users accept AI voices as natural conversation partners.
Real-Time Processing
Latency has dropped to conversational levels. Sub-second response times make voice interactions feel natural rather than laggy.
Making the Transition
For organizations currently relying on chatbots, the transition to voice does not have to be abrupt:
- Start with high-value use cases: Identify scenarios where voice would dramatically improve experience—product demos, complex support, sales conversations.
- Offer voice as an option: Let users choose between text and voice, observing preferences and outcomes.
- Measure rigorously: Track engagement, satisfaction, and conversion across both channels.
- Expand based on data: As voice proves its value, extend it to more use cases.
Solutions like Demogod make this transition straightforward, offering voice AI that integrates with existing websites without replacing infrastructure.
The Future is Conversational
The trajectory is clear. Voice interfaces are not replacing all text interaction—but for the highest-value customer touchpoints, voice is becoming the expectation rather than the exception.
Companies clinging to chatbot-only strategies will find themselves at a disadvantage. The organizations that embrace voice AI now will build capabilities, gather data, and refine experiences while competitors catch up.
The chatbot era taught us that customers want self-service options. The voice era is teaching us that they want those options to feel human. The best AI assistance does not feel like automation—it feels like conversation.
Ready to experience the difference? Try Demogod and see how voice AI agents create experiences that chatbots simply cannot match.
 DEMOGOD
DEMOGOD