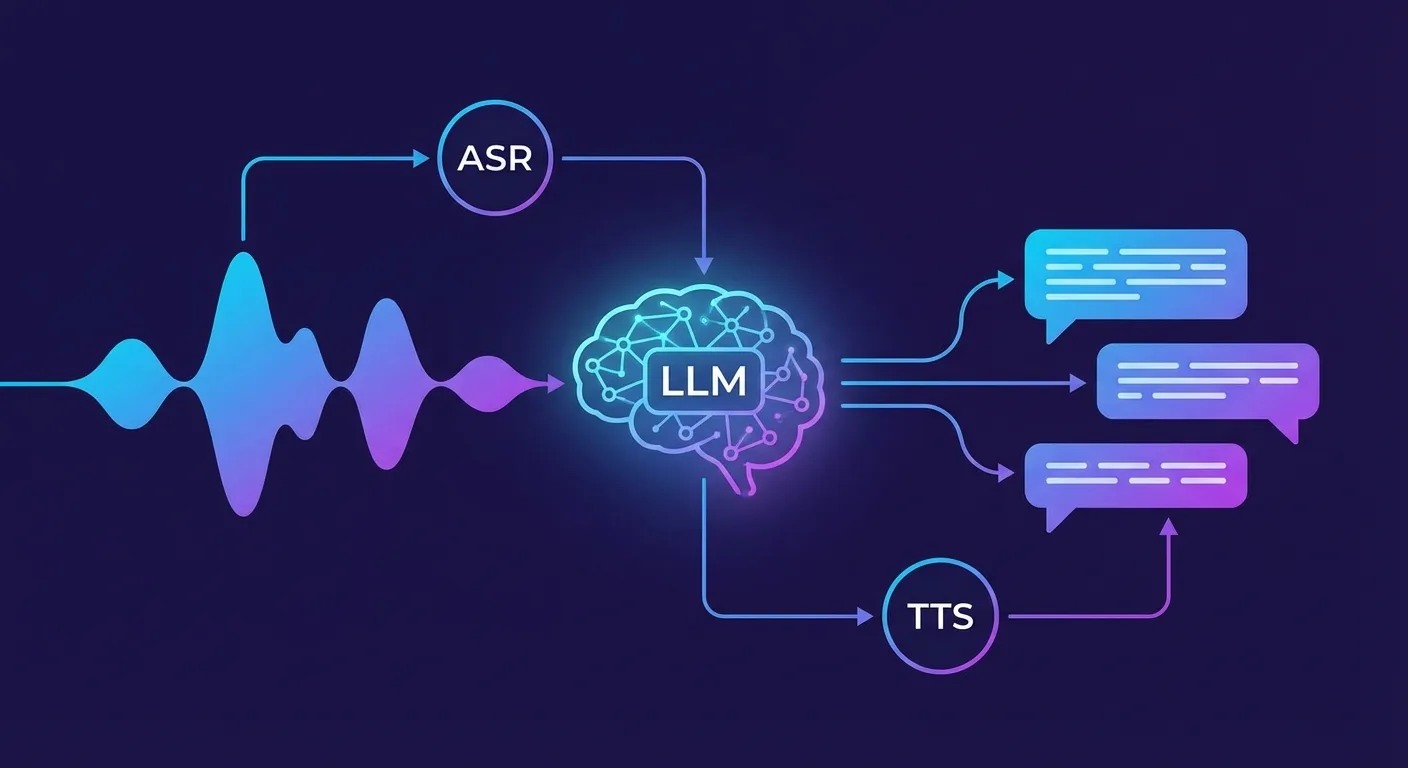
Voice AI agents need more than speech recognition and synthesis—they need intelligence. Large Language Models (LLMs) provide the reasoning, understanding, and generation capabilities that transform voice interfaces from simple command systems into genuine conversational experiences.
At Demogod, our voice agents combine real-time speech processing with LLM intelligence to guide users through product demos naturally. Here is how we connect speech to intelligence, and what you need to know about LLM integration for voice AI.
The Voice AI Intelligence Stack
A complete voice AI system has three core components:
- Speech Recognition (ASR): Converts spoken words to text
- Language Model (LLM): Understands intent, generates responses
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): Converts responses back to natural speech
The LLM sits at the center, receiving transcribed user input and producing responses that TTS voices. Its quality determines whether your voice agent feels like talking to a human or wrestling with a phone tree.
Choosing the Right LLM for Voice
Not every LLM works well for real-time voice applications. Key requirements:
Speed Over Everything
Voice conversations demand low latency. Users expect responses within 1-2 seconds of finishing their sentence. The LLM inference time directly impacts this—you need models that can generate initial tokens in under 500ms.
Streaming Output
The best voice experiences use streaming: sending LLM output to TTS as it generates, rather than waiting for the complete response. This requires models with streaming APIs and TTS systems that handle partial input.
Model Options
GPT-4o / GPT-4o-mini (OpenAI)
- Excellent reasoning and instruction-following
- Native streaming support
- GPT-4o-mini offers good balance of speed and capability
- Pricing: $0.15-$5.00 per million tokens depending on model
Claude 3.5 Sonnet / Haiku (Anthropic)
- Strong instruction-following and safety
- Haiku optimized for speed—ideal for voice
- Excellent at staying in character
- Pricing: $0.25-$3.00 per million tokens
Gemini 1.5 Flash (Google)
- Very fast inference
- Long context window (1M tokens)
- Good multimodal capabilities
- Competitive pricing
Llama 3.1 / Mistral (Open Source)
- Self-hostable for privacy/latency control
- Smaller models (7B-8B) achieve very low latency
- Requires infrastructure investment
- No per-token costs after setup
Prompt Engineering for Voice
Voice AI prompts differ from text chatbot prompts in crucial ways:
Keep Responses Concise
Long text responses feel natural to read but exhausting to hear. Your system prompt should emphasize brevity:
You are a voice assistant. Keep responses under 2-3 sentences.
Speak conversationally—avoid bullet points and lists.
If asked something complex, break it into follow-up questions.Avoid Visual Formatting
Markdown, bullet points, and code blocks make sense on screen but sound terrible spoken aloud. Instruct the model to use natural speech patterns instead.
Handle Interruptions
Users interrupt voice agents mid-sentence. Your prompt should prepare for this:
If the user interrupts, stop immediately and address their new input.
Do not try to complete your previous thought.Manage Uncertainty
Voice agents cannot show links or say "click here." When unsure, they should ask clarifying questions rather than providing uncertain information verbally.
Context Management for Conversations
Voice conversations accumulate context quickly. Managing this context affects both cost and response quality.
Conversation History
Include relevant prior turns but aggressively summarize older context. Recent messages matter most—a user asking "what about the price?" needs to know what product was just discussed.
System Context
For product demo agents, inject current page context into the prompt:
Current page: Pricing page
Visible elements: Basic ($29/mo), Pro ($99/mo), Enterprise (Contact us)
User is hovering over: Pro plan features listThis DOM-awareness lets the LLM give contextually relevant responses without the user explaining what they see.
Context Window Limits
Even with 128K+ context windows, including everything inflates costs and can slow inference. Implement sliding window strategies:
- Keep full system prompt
- Include last 5-10 conversation turns verbatim
- Summarize older history into a paragraph
- Include current page/application state
Function Calling for Actions
Voice agents need to do things, not just talk. LLM function calling enables this:
// Define available functions
functions: [
{
name: "navigate_to_page",
description: "Navigate to a different page on the website",
parameters: { page: "string" }
},
{
name: "click_element",
description: "Click on a specific element",
parameters: { element_id: "string" }
},
{
name: "fill_form",
description: "Fill in a form field",
parameters: { field: "string", value: "string" }
}
]When users say "show me the pricing page" or "add this to cart," the LLM generates function calls that your application executes. This creates truly interactive voice experiences.
Handling Latency
The perceived latency of voice AI comes from the full pipeline: ASR + LLM + TTS. Strategies to minimize it:
Parallel Processing
Start TTS as soon as the first LLM tokens arrive, not after complete generation. Stream everything.
Filler Responses
For complex queries requiring longer processing, generate immediate acknowledgments: "Let me look into that..." while the full response generates.
Predictive Caching
Pre-generate responses to common questions. If 40% of users ask "how much does it cost?" cache that response for instant playback.
Edge Deployment
Deploy LLM inference close to users. Services like Groq offer extremely fast inference, and edge deployments of smaller models can achieve sub-100ms response times.
Error Handling and Recovery
Voice interfaces cannot show error messages. Graceful degradation is essential:
ASR Failures
When speech recognition returns low-confidence results, have the LLM ask for clarification naturally: "I did not quite catch that—could you repeat?"
LLM Timeouts
If the LLM takes too long, interrupt with a fallback: "I need a moment to think about that. Can you tell me more about what you are looking for?"
Out-of-Scope Queries
Train the model to recognize and redirect off-topic questions: "I specialize in helping with our product demos. For billing questions, I can connect you with our support team."
Cost Optimization
Voice AI can consume significant LLM tokens. Optimization strategies:
Model Routing
Use smaller, faster models for simple queries and route complex ones to larger models. "What time do you close?" does not need GPT-4.
Response Caching
Cache responses to identical or semantically similar questions. Embedding-based similarity can identify cache hits.
Prompt Compression
Minimize system prompt tokens while maintaining behavior. Every token in the system prompt multiplies across all requests.
Privacy and Safety
Voice AI raises unique privacy considerations:
Data Handling
Decide whether to log transcripts. Users may share sensitive information verbally without realizing it is being recorded. Clear disclosure is essential.
Content Filtering
LLMs can generate inappropriate content. For voice, this is especially problematic—users cannot skim past offensive text like they can on screen. Implement robust content filtering.
Voice Cloning Concerns
If using custom voices, ensure proper consent and disclosure. Users should know they are speaking with AI.
The Complete Pipeline
Putting it all together, a voice AI request flows like this:
- User speaks → Audio captured via WebRTC
- Audio → ASR → Transcribed text (200-400ms)
- Transcribed text + context → LLM → Response tokens (streaming, 300-800ms to first token)
- Response tokens → TTS → Audio (streaming, begins immediately)
- Audio → User hears response
Total perceived latency: 800-1500ms for first audio, with response continuing to stream naturally.
Experience LLM-Powered Voice AI
The best way to understand LLM integration for voice is to experience it. Try Demogod—speak naturally, ask questions, and feel how LLM intelligence transforms voice interaction from command-and-response to genuine conversation.
The technology stack is finally mature enough to build voice AI that feels natural. Speech recognition, language models, and synthesis have converged to enable experiences that were science fiction five years ago. The companies building these experiences now will define how we interact with software for the next decade.
 DEMOGOD
DEMOGOD